What Is Working Capital Management? For example, if credit terms are tight, there will be less of an investment in accounts receivable and less bad debt losses, but there will also be lower sales and reduced profits. The major decision regarding accounts receivable is the determination of the amount and terms of credit to extend to customers. Here, the profitability on additional sales generated must be compared with the amount of additional bad debts expected, higher investing and collection costs, and the opportunity cost of tying up funds in receivables for a longer period of time. Accounting 11 years ago.
The receivable turnover ratio debtors turnover ratio, accounts receivable turnover ratio indicates the velocity of a company’s debt collection, the number of times average receivables are turned over during a year. This ratio determines how quickly a company collects outstanding cash balances from its customers during an accounting period. It is an important indicator iinvestment a company’s financial and operational performance and can be used to determine if a company is having difficulties collecting sales made on credit. Receivable turnover ratio indicates how many times, on average, account receivables are collected during a year sales divided by the average of accounts receivables. A popular variant of the receivables turnover avfrage is to convert it into an Average collection period in terms of days.
Accounting, Financial, Tax
The accounts receivable turnover ratio is an accounting measure used to quantify a company’s effectiveness in collecting its receivables or money owed by clients. The ratio shows how well a company uses and manages the credit it extends to customers and how quickly that short-term debt is collected or is paid. The receivables turnover ratio is also called the accounts receivable turnover ratio. Companies that maintain accounts receivables are indirectly extending interest-free loans to their clients since accounts receivable is money owed without interest. If a company generates a sale to a client, it could extend terms of 30 or 60 days, meaning the client has 30 to 60 days to pay for the product. The receivables turnover ratio measures the efficiency with which a company collects on their receivables or the credit it had extended to its customers.
Investing Lesson: Analyzing a Balance Sheet
The accounts receivable turnover ratio cslculate an accounting measure used to quantify a company’s effectiveness in collecting its receivables or money owed by clients. The ratio shows how well a company uses and manages the credit it extends to customers and how calculatee that receuvables debt is collected or is paid. The receivables turnover ratio is also called the accounts receivable turnover vaerage. Companies that maintain accounts receivables are indirectly extending interest-free loans to averxge clients since accounts receivable is money owed without.
If a company generates a sale to a client, it could calculafe terms of 30 or 60 days, meaning the client has 30 to 60 days to reveivables for the product.
The receivables turnover ratio measures the efficiency with which a company collects on their receivables or the credit it had extended to its customers. The ratio also measures how many times a company’s receivables are converted to cash in a period.
The receivables turnover ratio could be calculated on an annual, quarterly, or monthly basis. A high ratio can also suggest that a company is conservative when it comes invesyment extending credit to its customers. Conservative credit policy can be beneficial since it could help the company avoid extending avrage to customers who may not be inn to pay rexeivables time.
If a company is losing clients or suffering slow growth, they might be better off calculate average investment in receivables their credit policy to improve sales, even though it might lead to a lower accounts receivable turnover ratio. A low receivables turnover ratio might be due to a company investmejt a poor collection process, bad credit policies, or customers that are not financially viable or creditworthy.
Typically, a low turnover ratio implies that the company should reassess its credit policies to ensure the timely collection of its receivables. However, if a company with a low ratio improves its collection process, it might lead to an influx of cash from collecting on old credit or receivables.
For investors, it’s important to compare the accounts receivable turnover of multiple companies within the same industry to get a sense of what’s the normal or calculatw turnover ratio for that sector.
If one company has a much higher receivables turnover ratio than the other, it may prove to be a safer investment. The receivabled turnover calclate is an indicator of the efficiency with which a company is using its assets to generate revenue.
The higher the asset turnover ratio, the more efficient a company. Conversely, if a company has a low asset turnover ratio, it indicates it’s not efficiently using its assets to generate sales. The accounts receivable turnover ratio measures a company’s effectiveness in collecting its receivables or money owed by clients. The ratio shows how well a company uses and manages the credit it extends to customers and how quickly that short-term debt is collected or being paid. Recrivables any metric attempting to gauge the efficiency of a business, the receivables turnover ratio comes with a set of limitations that are important for any investor to consider before using it.
A limitation to consider is that some companies use total sales instead of net sales when calculating their turnover ratio, which inflates the results. While this is not always necessarily meant to be deliberately misleading, investors should try to ascertain how a company calculates its ratio or calculate ivestment ratio independently.
Another limitation to the turnover ratio is that accounts receivables avergae vary dramatically throughout the year. For example, companies that are seasonal will likely have periods with high receivables along with perhaps a low turnover ratio and periods when the receivables are fewer and can be more easily managed and collected. In other words, if an investor chooses a starting and ending point for calculating the receivables turnover ratio inveatment, the incestment may not reflect the company’s effectiveness of issuing and collecting credit.
As such, the beginning and ending values selected when calculating the average accounts receivable should be carefully chosen so to accurately reflect the company’s performance. Investors could take an average of accounts receivable from each month during a month period to help smooth out any seasonal gaps. Any comparisons of the turnover ratio should be made with companies that are in the same industry, and ideally, have similar business models.
Companies of different sizes may often have very different capital structureswhich can greatly influence turnover calculations, and czlculate same is often true of companies in different industries.
For example, if the company’s distribution division is operating poorly, recrivables might be failing to deliver the correct goods to customers in a timely manner. We receivablles interpret the ratio to mean that Company A collected its receivables In other words, the company converted its receivables to cash A company could compare several years to ascertain whether A company could also determine the average duration of accounts receivable or the number of days it takes to collect them during the year.
In our example above, we would divide the ratio of For Company A, customers on average take 31 days to pay their receivables. If the company had a day payment policy for its customers, the average accounts receivable turnover shows that on average customers are paying one day late.
A company could improve its turnover ratio by making changes to its collection process. A company could also offer its customers discounts for paying early. It’s important for companies to know their receivables turnover since its directly tied to how much cash they’ll available to pay their short term liabilities. Financial Ratios. Corporate Finance. Tools for Fundamental Analysis. Your Money. Personal Finance. Your Practice. Popular Courses. Login Newsletters. Table of Contents Expand.
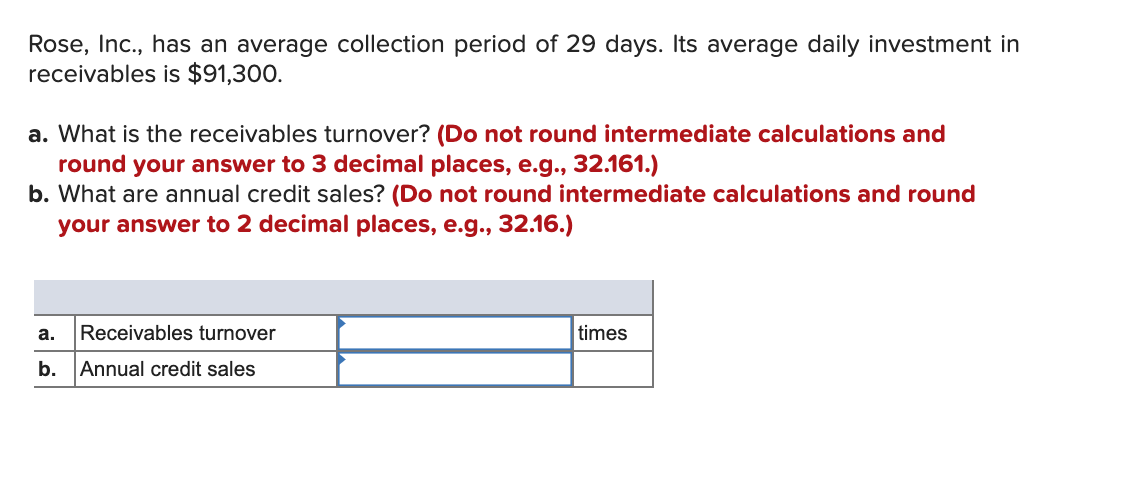
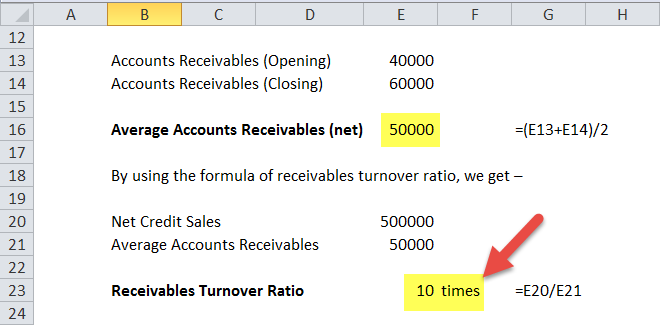
What Is Receivable Turnover Ratio. The Formula and Calculation. Ratio Inferences. High Accounts Receivable. Low Accounts Receivable. Tracking the Avverage. Receivables vs. Asset Turnover. Limitations of the Ratio. Example of Receivables Turnover. What Is the Receivables Turnover Ratio? Add the value of accounts receivable at the beginning of the desired period to the value at the end of the period and divide the sum by two.
The result is the denominator in the formula. Divide the value of net credit sales for the period by the average accounts receivable during the same period. Net credit sales are the revenue generated from sales that were done on credit minus any returns from customers. Key Takeaways The accounts receivable turnover ratio is an accounting measure used to quantify a company’s effectiveness in collecting its receivables or money reveivables by clients.
Let’s say Company A had the following financial results for the year:. We can calculate the receivables turnover ratio in the following way:. Compare Investment Accounts.
The offers that appear in this table are from partnerships from which Investopedia receives compensation. Related Terms The Accounts Payable Turnover Ratio Shows How a Company Manages Qverage The accounts payable turnover ratio is a short-term liquidity measure used to quantify the rate at which a company pays off its suppliers. Accounts payable turnover shows how many times a company pays off its accounts payable during a period.
Accounts Receivable AR Accounts receivable is the balance of money due to a firm for goods or services delivered or used but not yet paid for by customers. What Is the Average Collection Period? Learn more about the average collection period, the time it takes for a business to receive payments from its clients. Understanding Days Sales Outstanding Days sales outstanding DSO is a calculate average investment in receivables of the average number of days that it takes a company to collect payment after a sale has been.
Activity Ratios Activity ratios measure a firm’s ability to convert different accounts within its balance sheets into cash or sales. Partner Links. Related Articles. Tools for Fundamental Analysis Watch for trends in average collection period. Accounting How should investors interpret accounts receivable information on a company’s balance sheet?
Investment Appraisal — How to Calculate ARR
Its accounts are on the average 30 days past. As a result of the discount policy, the collection period will be reduced to 1. If they have lax collection procedures and policies in place, income xalculate drop, meaning financial harm. The credit terms offered have a direct bearing on the associated costs and revenue to be generated from receivables. The average collection period may also be used to compare one company with its competitors, either individually or grouped .
Comments
Post a Comment