If you drive from home to your regular place of employment, it’s not deductible, but if your employer requires that you work somewhere else, this mileage may be deductible. It includes the entire city or general area in which your business or work is located. The standard mileage rate deduction for the tax year was However, an exception applies to members of the Armed Forces on active duty moving under orders to a permanent change of station. Share to facebook Share to twitter Share to linkedin. And you can still claim a deduction for miles driven for purposes of medical care. The medical expense deduction survived the TCJA and the rate for these miles is 18 cents in 20 cents per mile beginning on January 1,
Who is likely to be affected
If you must drive as part of your job, you may be qualified to deduct the costs on your federal income tax return. If you qualify, get ready to document your travels as supporting evidence in the event your taxes are audited. A taxpayer can take the mileage deduction for travel mileage rate tax invest the office to a work site, from the office to a second place of business, or for driving on business-related errands. Milsage addition, a taxpayer can include trips made to meet with clients, txa to the airport, visiting customers for business, or searching for a new job in the same industry. The Internal Revenue Service IRS requires a taxpayer to record the business vehicle’s odometer reading at the beginning of the tax year.
We use cookies to collect information about how you use GOV. We use this information to make the website work as well as possible and improve government services. You can change your cookie settings at any time. This publication is licensed under the terms of the Open Government Licence v3. To view this licence, visit nationalarchives. Where we have identified any third party copyright information you will need to obtain permission from the copyright holders concerned.
If you must drive as part of your job, you may be qualified to deduct the costs on your federal income tax return. If you qualify, get ready to document your travels as supporting evidence in the event your taxes are audited.
A taxpayer can take the mileage deduction for travel from the office to a work site, from the office to a second place of business, or for driving on business-related errands. In addition, a taxpayer can include trips made to meet with clients, going to the airport, visiting customers for business, or searching for a new job in the same industry. The Internal Revenue Service IRS requires a taxpayer to record the business vehicle’s odometer reading at the beginning of the tax year.
This will be documented on Form If the vehicle is purchased during the year and is not new, the taxpayer must record the odometer reading from the first day it is deployed.
If you choose the standard mileage deduction, you must keep a log of miles driven. The IRS is quite specific on this point:. If you choose the actual expense deduction, the mileage log isn’t needed. Instead, keep copies of relevant receipts and documentation. Each document must include the date, dollar amount of the service or service purchased, and description of the product or service needed.
At the end of the tax yearthe taxpayer must record the ending odometer reading. This figure is used in conjunction with the odometer reading at the beginning of the year to calculate the total mileage rate tax invest driven in the car for the year. The information, including what percentage of miles driven were for business purposes, is required on Form When completing your tax returns, you’ll list the total amount of miles driven on FormLine This figure is calculated by the standard mileage rate for the year to determine the dollar deductible.
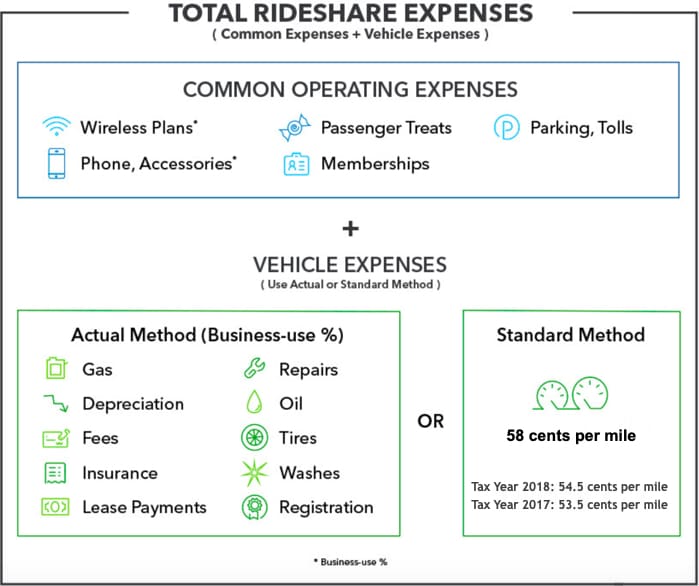
If you’re using the actual expenses method, you’ll need to organize the receipts of the expenses into groups including gasoline, oil, repairs, insurance, vehicle rentals, and depreciation. If documentation is requested from the IRS to substantiate the mileage deduction, the taxpayer should make a copy of the records and file a personal copy.
Charitable Donations. Small Business Taxes. Your Money. Personal Finance. Your Practice. Popular Courses. Login Newsletters. Key Takeaways There are two methods of claiming the mileage deduction. To use the standard deduction, you must keep a log of the miles you drive for work.
To use the actual expense method, you must save all the receipts of expenses related to driving for work. A taxpayer can choose between two methods of accounting for the mileage deduction amount:. The standard mileage deduction requires only that you maintain a log of qualifying mileage driven.
For tax yearthe standard mileage deduction is 58 cents per mile. That’s up 3. The deduction for actual vehicle expenses requires that you retain all receipts and other relevant documentation relating to the costs of driving.
At the start of each trip, the taxpayer must record the odometer reading and list the purpose, starting location, ending location, and date of the trip. At the conclusion of the trip, the final odometer must be recorded and then subtracted from the initial reading to find the total mileage for the trip.
This log must be maintained regularly. The IRS does not care for ballpark figures. You must retain the documentation relating to a mileage deduction for at least three years. To keep it all straight, create a new log for each tax year. Compare Investment Accounts. The offers that appear in this table are from partnerships from which Investopedia receives compensation. Related Articles. Partner Links. The Standard Mileage Rate is a default per-mile amount that taxpayers who use mileage rate tax invest vehicles for business purposes can claim on their tax returns.
Mileage Allowance A mileage allowance is the rate at which the IRS suggets tax payers deduct miles driven as an expense for approved purposes. It primarily focuses on itemized deductions for Schedule A.
Travel Expenses Definition Travel expenses are costs incurred while traveling specifically for the purpose of conducting business-related activities.
2018 Tax Changes For Businesses (2018 Business Tax Rules Explained!) Tax Cuts and Jobs Act 2018
In this case, you would claim your business mileage on Schedule C. And yes, you must itemize to claim these miles. Taxes Tax Filing Basics. Read More. It was a horrible experience. If you combine your business travel with mileage rate tax invest sort of personal travel, like running errands, those miles are not deductible. Years ago, I found myself sitting in law school in Moot Court wearing an oversized itchy blue suit. Health Insurance. By William Perez. What’s deductible and what’s not begins with your «tax home. Your employer can’t reimburse you for the mileage, however, and you can’t deduct expenses associated with traveling from your own home to your tax home. The IRS issued guidance on this issue, and you can find out more. In a desperate attempt to avoid anythi Beginning on January 1,the standard mileage rates for the use of a car, van, pickup or panel truck will be:. However, if you are self-employed there may be some deductions you can still take for mileage. What Is Mileage Allowance? You can claim a deduction for the balance over this .

Comments
Post a Comment