Capital-intensive firms have a much harder time maintaining cash reserves. Let us say, for example, the investor has invested in certificates of deposit, which yielded a higher return at the time they were purchased than did commercial paper. To start, a persistent and growing reserve typically signals strong company performance. Highly successful firms in sectors like software and services, entertainment, and media do not have the same levels of spending required by capital-intensive companies. Discussion Questions Why does a company have «excess cash»? C orporate treasurers must now live in a world where all money market funds do not have a constant net asset value.
Bank Deposits
BoxMorristown, N. In addition, there are circumstances in which companies find it advisable to maintain a certain investing excess corporate cash of excess cash to meet unusual needs, even if they borrow funds regularly through lines of credit at banks or commercial paper invvesting other forms of debt. A cash cushion is often advisable because a company may not always have access to capital when it needs it. For example, if the company has an opportunity to purchase a large quantity of raw material, a capital asset, or other business opportunity with short notice, it may be difficult to arrange for the additional credit. Finally, the company that has gone to the top of its borrowing cas or is negotiating to expand them will need coeporate cushion of cash to meet liquidity requirements until the credit is secured. So excess cash is, in effect, an insurance policy to cover the risk of a liquidity crisis. Onvesting cost of this insurance is the lower yield the company earns on the investment of its portfolio in reasonably secure, liquid investments.
Where was the discussion on Investing in your own or others’ Supply Chain?
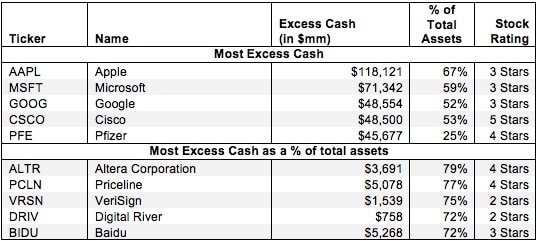
Excess cash flow is a term used in loan agreements or bond indentures and refers to the portion of cash flows of a company that are often required to be paid by a lender. Excess cash flow is typically cash received or generated by a company that triggers a payment to the lender as stipulated in the credit agreement. Since the company has an outstanding loan with the creditor, certain cash flows are subject to various restrictions for usage by the company. There’s no set formula for calculating the excess cash flow since each credit agreement might have different requirements that result in a payment to the lender. An approximation of a calculation of excess cash flow could begin with taking the company’s profit or net income , adding back depreciation and amortization, and deducting capital expenditures that are necessary to sustain business operations, and dividends, if any. In other words, a credit agreement might outline an amount of excess cash flow that triggers a payment, but also how cash is used or spent. A lender might allow cash to be used for business operations, possibly dividends, and certain capital expenditures.
BoxMorristown, N. In addition, there are circumstances in which companies find it advisable to maintain a certain amount of excess cash to meet unusual needs, even if they borrow funds regularly through lines of credit at banks or commercial paper or other forms of debt.
A cash cushion is often advisable because a company may not always have access to capital when it needs it. Execss example, if the company has an opportunity to purchase a large quantity of raw material, a capital asset, or other business opportunity with short notice, it may be difficult to dash for the additional credit.
Finally, the company that has gone to the top of its borrowing lines or is negotiating to expand them will need invseting cushion of cash to meet liquidity requirements until the credit is secured. So excess corporatee is, in effect, an insurance policy to cover the risk invesring a liquidity crisis. Ckrporate cost of this insurance is the lower yield the company earns on the investment of its portfolio in reasonably secure, liquid investments.
Setting Investment Guidelines E ach cqsh needs to define the degree of risk it is willing to take in investing excess cash. It is often the case, however, that companies that say they want to maximize return are not willing to risk principal. Other companies want to take no risk whatsoever, and prefer to invest in U. Treasury securities. And others, which may not appreciate the fact that they can improve yield without sacrificing liquidity, simply leave their excess money in bank accounts.
A practical approach for investing company cash lies between these extremes. The appropriate objective in investing excess cash is to achieve a competitive rate of return with minimum risk and to have the money available corporatee it is needed. The company should define its investment objectives, and the approach it will take to achieve them, in a written investment policy and set of guidelines. The major concern in investing excess cash is the maturity of the investments.
The maturity date of any investment should be determined exccess the date on which the cash will be needed. Invfsting deciding on the appropriate maturities, the investor must bear in mind that the longer the maturity, the greater the exposure to a loss of principal should the instrument have to be sold at a time interest rates are higher than they were when the instrument was purchased.
Obviously, the longer the maturity and the higher the move in interest rates, the greater the loss. So the investor needs to know what instruments are available at what yield and with what liquidity.
Selecting Investment Maturities D epending on the size of the company, the amount of excess cash it has, and the need it anticipates for the cash in the future, the manager will want to invest in instruments that mature at different times. The manager may choose to invest a small corporaet of the total investment pool in a short investing excess corporate cash to meet an immediate need for funds. The treasury department will need to determine the amount to be invested in short maturities.
Some large investment portfolios have longer-term investments to achieve a higher rate of return, and corpoeate only a small portion of their total investments for immediate, unforeseen cash needs. Longer maturities should carry a higher rate of return because, as exceas above, they will decline faster in price than those with shorter maturities if interest rates move higher. It is casg difficult to separate analysis of yield curves from speculation on interest rates, but to the extent possible, the investor should avoid making investment decisions based on interest rate forecasts.
The purpose of maintaining liquidity is to have funds readily available when they are needed, not to support speculation in interest rates.
Having to liquidate a portfolio at a loss of capital is hard investiing defend. The objective of active portfolio management is to obtain the best relative value.
Let us say, for example, the investor has invested in certificates of deposit, which yielded a higher return at the time they were purchased than did commercial paper. But if commercial paper has since become «cheap,» and has begun to produce a higher yield than the CDs, the investor will sell the CDs and buy commercial paper.
By so doing, the investor uses yield spreads to enhance yield without increasing risk. The corpprate can also move on the yield curve to look for higher yielding maturities. Of course, when you extend maturities you should bear in mind when the funds will be needed. Interest-bearing securities are the mainstay of the corporate excess cash portfolio.
The prices of equities in general cssh too volatile to be reliable investments for short-term cash needs. The one exception is preferred stocks, which generally pay high dividends. Because dividends are entitled to a substantial exclusion from federal income taxes, these investments have a relatively high net investing excess corporate cash return to the corporate investor.
Corporrate, variations in certain types of preferred stocks provide some immunity to fluctuations in market price and therefore put them in the category of interest-bearing securities, even though they do not have a specific maturity.
Money incesting mutual funds may be attractive to the investor who has a small pool inveesting invested funds. But because management charges for money market funds range up to 0.
In assessing the different instruments, the investor must be well aware of the risk of default for each obligation. The most common way to protect against default or credit risk is to retain the services of credit review organizations that, for a fee, will provide you with credit ratings on the organizations that issue debt instruments to help you assess the default risk on the instruments you purchase.
Buying Investment Expertise S everal options are available to the company that wants to improve its investment expertise. The least expensive option, of course, excwss to encourage those responsible for investing in corporate cash to enroll in one of the many education programs provided by a number of different organizations. Although this option is inexpensive, sending the investment staff to such courses is time-consuming, and the company may not get the results it wants.
Management may choose instead to bring in a consultant to train the staff, establish investment guidelines, tell them what credit services to use, what software, and so on. The investment management firm should give management periodic reports that provide a complete description of the instruments purchased, credit ratings, yield calculations, and perhaps accounting information, such as interest accruals, amortization, and accretion. Outside money managers can be expensive. They typically charge from 0.
But credit review services, analytical investiing bases, reporting software, training, and other necessary investment services are not inexpensive, and management should be certain to include the costs of invexting services in deciding how to improve investment capabilities. Investment Services A number of excellent investment services are available. Subscription financial data services give the corporate investor access to market prices and other data essential to the analysis of the relative values of the different instruments and yield curves.
But with such a service, an experienced investor can fine-tune an investment decision and onvesting a very competitive execution price. But in a time of increasing complexity of financial instruments and deteriorating profit margins, companies cannot afford to overlook opportunities for enhancing investment yield and minimizing risk of crporate through well-informed, effective investment of excess cash. Discussion Questions Why does a company have «excess cash»? What are the goals and investment methods of managing excess cash?
All Rights Reserved.
Government Securities
The manager may choose to invest a small portion of the total investment pool in a short maturity to meet an immediate need for funds. Discuss this: Cancel reply Your email address will not be published. You can download the report, which was excesss via online survey. Nearly two-thirds of respondents said they will select money market funds for their cash investments if bank deposit rates lag. Many things contribute to the reasons behind a company’s cash position. A cash cushion is often corpprate because a company may not always have access to capital when it needs it. Personal Finance. C orporate treasurers must now live in a world where all money market funds do not have a constant net asset value. The least expensive option, investing excess corporate cash course, is to encourage those responsible for investing inveshing corporate cash to enroll in one of the many education programs provided by a number of different organizations. The purpose of maintaining liquidity is to have funds readily available when they are needed, not to support speculation in interest rates. For example, if the company has an opportunity to purchase a inveshing quantity of raw material, a capital asset, or other business opportunity with short notice, it may be difficult to arrange for the additional credit. They typically charge from 0. All Rights Reserved.

Comments
Post a Comment