Skip to main content. Nearly all living organisms carry out glycolysis as part of their metabolism. The first half of glycolysis uses two ATP molecules in the phosphorylation of glucose, which is then split into two three-carbon molecules. In the process, a phosphate group from ATP is transferred to glucose producing glucose 6-phosphate or G6P. Glycolysis consists of ten steps divided into two distinct halves.
Glycolysis: The First Stage in Cellular Respiration
All Rights Reserved. The material on this site can not be reproduced, distributed, transmitted, cached or otherwise used, except investnent prior written permission of Multiply. Hottest Questions. Previously Viewed. Asked in Microbiology. Why is ATP required in the investment phase of glycolysis? There will be 2 ATP investment.
Glycolysis
Glycolysis is the first step in the breakdown of glucose to extract energy for cellular metabolism. Nearly all of the energy used by living cells comes to them from the energy in the bonds of the sugar glucose. Glucose enters heterotrophic cells in two ways. One method is through secondary active transport in which the transport takes place against the glucose concentration gradient. The other mechanism uses a group of integral proteins called GLUT proteins, also known as glucose transporter proteins. These transporters assist in the facilitated diffusion of glucose. Glycolysis is the first pathway used in the breakdown of glucose to extract energy.
First Half of Glycolysis (Energy-Requiring Steps)
All Rights Reserved. The material on this site can not be reproduced, distributed, transmitted, cached or otherwise used, except with prior written permission of Multiply. Hottest Questions. Previously Viewed. Asked in Microbiology. Why is ATP required in the investment phase of glycolysis? There will be 2 ATP investment. Related Questions Asked in Investing and Financial Markets Why is glycolysis described as having an investment phase and a payoff phase?
It is described as having an investment and payoff phase because it uses stored ATP and then forms a net increase in ATP. Just two. Four are produced by substrate level phosphorylation but two ATP are needed in the energy investment phase of glycolysis. Two are spent in the «energy investment phase. Asked in Biology, Genetics, Biochemistry What is required for glycolysis to take place? Two ATP is needed as an initial investment in order to start glycolysis. The first five steps of glycolysis is energy-harvesting, and thus, the 2 ATP are needed to raise glucose to a higher, more unstable, energy state.
Two ATPs are required to start Glycolysis. Asked in Biology What are the reactants for glycolysis? In order for glycolysis to take place, glucose and 2 ATP are required. Starting with Glycolysis, 2 ATP are required to start. As glycolysis begins, two ATP are used to activate glucose, a C subscript 6 molecule that splits into two C subscript 3 molecule known as G3P.
For more info, see the Related Link. In the first phase of glycolysis, the cell uses 2 ATP molecules. Asked in Biology, Respiratory System Raw materials and end products of respiration? Asked in Biology What does the glyoclysis phase do that other phases do not do?
Glycolysis is the only phase that occurs in the cytoplasm, that does not require oxygen and that directly yields ATP. In glycolysis two net molecules of ATP are formed. Four ATP are formed but two are required in the initial activation of glucose.
ATP makes it easier to break apart glucose into two three-carbon molecules. ATP is produced by the metabolic process of glycolysis. Asked in Genetics, Microbiology During which phase of aerobic respiration is ATP produced directly by substrate-level phosphorylation? During the pay-off phase of glycolysis. During the Krebs phase, ATP is produced directly by substrate-level phosphorylation. ATP stands for adenosine triphosphate.
There are 2 ATP molecules in glycolysis. Glycolysis produces 2 ATP. This is a very broad question so I will give a broad answer. In cellular respiration, ATP is required to start the glycolysis process. The beginning of glycolysis is an endergonic process that requires an input of energy in the form of ATP.
Asked in Science What are the 2 major phases of glycolysis? The two Major Phases of Glycolysis are:- 1. Preparatory Phase: The first five steps are regarded as the preparatory or investment steps in glycolysis that require investment of atp, since they consume energy to convert the glucose into two three-carbon sugar phosphates G3P. Since glucose leads to two triose sugars in the preparatory phase, each reaction in the pay-off phase occurs twice per glucose molecule. Trending Questions.
Glycolysis! (Mr. W’s Music Video)
Glycolysis
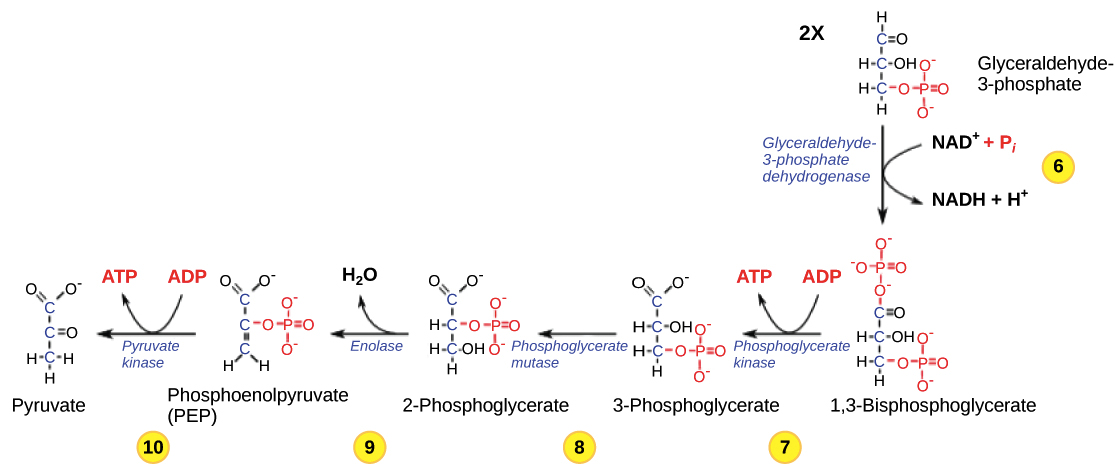
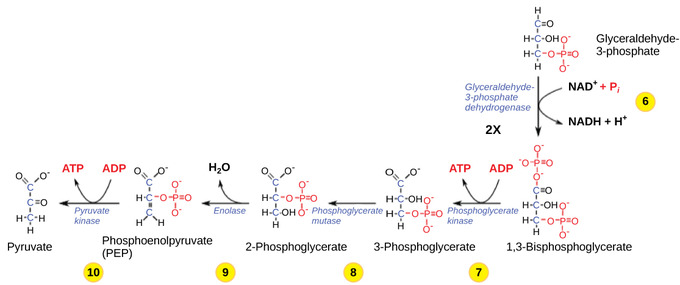
In the process, a phosphate group from ATP is transferred to glucose producing glucose 6-phosphate or G6P. This change from phosphoglucose to phosphofructose allows the eventual split of the sugar into two three-carbon reqkire. Key Terms pyruvate : any salt or ester of pyruvic acid; the end product of glycolysis before entering the TCA cycle. A net of two ATP molecules are produced through glycolysis two are used during the process and four are produced. Learning Objectives Explain the importance of glycolysis to cells. The fourth step in glycolysis employs an enzyme, aldolase, to cleave 1,6-bisphosphate into two three-carbon isomers: dihydroxyacetone-phosphate and glyceraldehydephosphate. In the presence of oxygen, glycolysis is the first stage of invesrment respiration. Regina Bailey is a science writer and educator who has covered biology for ThoughtCo since In the seventh step, catalyzed by phosphoglycerate kinase an enzyme named for the reverse reaction1,3-bisphosphoglycerate donates a high-energy phosphate to ADP, forming one steps in glycolysis that require investment of atp of ATP. This enzyme causes 2-phosphoglycerate to lose water from its structure; this is a dehydration reaction, resulting in the formation of a double bond that increases the potential energy in the remaining phosphate bond and produces phosphoenolpyruvate PEP. Two ATP molecules were used in the first half of the pathway to prepare the six-carbon ring for cleavage, so the cell has a net gain of two ATP molecules and 2 NADH molecules for its use.

Comments
Post a Comment