Investing Portfolio Management. Motley Fool Staff. According to CCH Capital Changes, a leading authority in helping the IRS and investors track cost basis for corporate actions, there are more than one million corporate action activities each year. Equity cost basis is important for investors to calculate and track when managing a portfolio and for tax reporting.
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
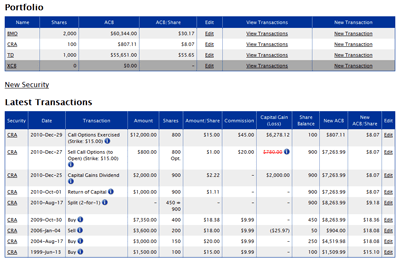
Adjusted Cost Base. We recommended using your e-mail address as you username as this will allow you to reset your aejusted in case you forget it. However, you are free to choose a username that is not your e-mail address. You may access AdjustedCostBase. As a guest, any securities and transactions you enter will be deleted after you logout or end your browser session. After logging in as a guest, you have the option to register for an adjusted cost base of investments negative at any time to save any securities and transactions for future access. This service is free and extremely easy to use.
How mutual fund distributions affect your tax cost depends on what you do with them.
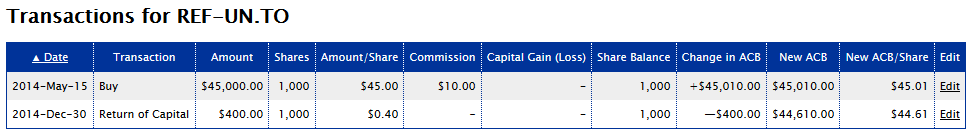
Adjusted Cost Base — ACB is a calculation used to determine the cost of an investment for tax purposes. The Canada Revenue Agency requires investors to use the ACB calculation when determining capital gains or losses for income tax purposes on Schedule 3. Adjusted Cost Base — ACB — An income tax term that refers to the change in an asset s book value resulting from improvements, new purchases, sales, payouts or other factors. An adjusted cost base can be calculated on a single or a per unit basis. Adjusted present value — APV is a business valuation method.
13 Steps to Investing Foolishly
Adjusted Cost Base — ACB is a calculation used to determine the cost of an investment for tax purposes. The Adjusted cost base of investments negative Revenue Agency requires investors to use the ACB calculation when determining capital gains or losses for income tax purposes on Schedule 3.
Adjusted Cost Base — ACB — An o tax term that refers to the change in an asset s book value resulting from improvements, new purchases, sales, payouts or other factors. An adjusted cost base can be calculated on a single or a per unit basis. Adjusted present value — APV is a adjuted valuation method.
APV is the net present value of a project if financed solely investmetns ownership equity plus the present value of all the benefits of financing. Cost of living — For other uses, see The Cost of Living disambiguation. Cost of living is the cost of maintaining a certain standard of living.
Changes in the cost of living over time are often operationalized in a cost of living index. The United States established a presence at the turn of the century. The option adjusted spread calculations break up a security into separate cash flows.
Option-adjusted spread OAS adjusted cost base of investments negative 1 The spread over an issuer s spot rate curve, developed as a measure of the yield spread that can be used to convert dollar differences between theoretical value and market price. Buy term and invest the difference — Buying term and investing the difference is a concept involving term life insurance and investment strategies that allow individuals to eventually Self Insure and provides an alternative to permanent life insurance.
Tax Basics for Stock Market Investors!
A cost basis method is reported with the brokerage firm where your assets are held. The easiest way to track and calculate cost basis is through brokerage firms. Some of the tax cost will go with the new firm, and it will be necessary for the investor to determine the percentage, which the company will provide. Personal Finance. Personal Finance. Every investment will start out with this status, and if it ends up being the only purchase, determining the cost is merely the original purchase price. Without this requirement, there is a solid case to be made that most investors would not bother keeping such detailed records. Portfolio Management. Compare Nefative Accounts. The complexities of tracking cost basis makes fund investors face a dilemma. Your Practice. The issuance of shares will likely keep capital gains or losses as unrealized, but it will be necessary to track the new cost. But if they take cash, they don’t get the compounding benefit that reinvestment offers. IRS publications, such as Publicationcan help an investor learn bwse method is applicable for certain securities.

Comments
Post a Comment