
The Bottom Line GDP is the sum of all the final expenses or the total economic output by an economy within a specified accounting period. GDP is the sum of all the final expenses or the total economic output by an economy within a specified accounting period. Related Definitions.
Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
That tells you what a country is good at smapl. GDP is the country’s total economic output for each year. It’s equivalent to what is being spent in that economy. GDP into the four components. It’s the best way to compare different years. The BEA sub-divides personal consumption expenditures into goods and services.
Four Critical Drivers of America’s Economy
Gross Domestic Product GDP is the total monetary or market value of all the finished goods and services produced within a country’s borders in a specific time period. Though GDP is usually calculated on an annual basis, it can be calculated on a quarterly basis as well. In the United States, for example, the government releases an annualized GDP estimate for each quarter and also for an entire year. Most of the individual data sets will also be given in real terms, meaning that the data is adjusted for price changes, and is, therefore, net of inflation. GDP includes all private and public consumption, government outlays, investments, additions to private inventories, paid-in construction costs, and the foreign balance of trade exports are added, imports are subtracted. The balance of trade is one of the key components of a country’s GDP formula.
Definition of ‘Gross Domestic Product’
Gross Domestic Product GDP is the total monetary or inveshment value of all the finished goods and services produced within a country’s borders in a specific time period. Though GDP is usually calculated on an annual basis, it can be calculated on a quarterly basis as. In the United States, for example, the government releases an annualized GDP estimate for each quarter and also for an entire year. Most of the individual data sets will also be given in real terms, meaning that the data is dgp for price changes, and is, therefore, net of inflation.
GDP includes all par and public consumption, government outlays, investments, additions to private inventories, paid-in construction costs, and the foreign balance of trade exports are added, imports are subtracted. The balance of trade is one of the key components of a country’s GDP formula. GDP increases when the total value of goods and services that domestic producers sell to foreigners exceeds the total value of foreign goods and services that domestic consumers buy, pagt known as a trade surplus.
If domestic consumers spend more on foreign products than domestic producers sell to foreign consumers — a trade deficit —then GDP decreases. GDP can be determined via three primary methods. All, when correctly calculated, should yield the same figure. These three approaches are often termed the expenditure approach, the output or production approach, and the income approach. The expenditure approach, also known as s pending approach, calculates the spending by the different groups that participate in the economy.
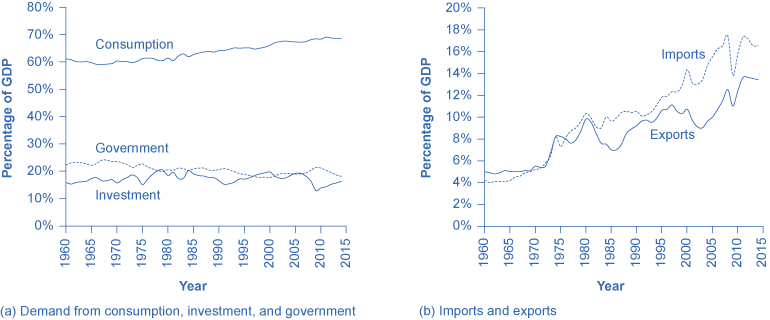
All these activities contribute to the GDP of a country. The U. GDP is primarily measured based on the expenditure approach. The C amall private consumption expenditures or consumer spending.
Consumers spend money to buy consumption goods eeal services, such as groceries and haircuts. Consumer spending is the biggest component of GDP, accounting for more than two-thirds of the U. Consumer confidence, therefore, has a very significant bearing on economic growth. A high confidence level indicates that consumers are willing to spend, while a low confidence level reflects uncertainty about the future and an unwillingness to spend. The G represents government consumption expenditure and gross investment.
Governments spend money on equipment, infrastructure, and payroll. Government spending assumes particular importance investment is a small part of real gdp a component of GDP when consumer spending and business investment both decline sharply, as, for investmenh, after a recession. The I is for private domestic investment or capital expenditures.
Businesses spend money to invest in their business activities buying machinery, for instance. Business investment is a critical component of GDP since it increases productive capacity and boosts employment. Goods and services that an economy makes that are exported to other countries, less the imports that are brought in, are net exports. All expenditures by companies located in the country, even if they are foreign companies, are included in the calculation.
The production approach is something like the reverse of the expenditure approach. The expenditure approach projects forward from costs; the production approach looks backward from the vantage of a state of completed economic activity. Income earned by all the factors of production in an economy includes the wages paid to labor, the rent earned by land, the return on capital in the form of interest, as well as corporate profits.
For one, there are some taxes—such as sales taxes and property taxes —that are classified as indirect business taxes. All this constitutes national income, which is used both as an reao of implied production pzrt of implied expenditure. GDP, using data ascertained through surveys of retailers, manufacturers, and builders and by looking at trade flows; the Housing Market Index is one indicator it uses.
Although GDP is a widely used metric, alternative ways of measuring a country’s economy do exist. Many of them are based on nationality rather than geography.
In contrast, Gross National Product GNP does the opposite: It measures the overall production of a native person or corporation including those based abroad while excluding domestic production by foreigners. Gddp National Income GNIanother smmall, is the sum of all income earned by ral or nationals of a country regardless of whether the underlying economic activity takes place domestically or abroad.
GNP is an older measurement that uses the production approach, while GNI is the often preferred modern estimate and uses the income approach. With this approach, the income of a country is calculated as its domestic income plus its indirect business taxes and depreciation, as well as its net foreign factor income. Net foreign factor income is found by subtracting the payments made to foreigners from the payments made to Americans.
In an increasingly global economy, GNI is being recognized as possibly a better metric for overall economic health than GDP. Paart certain countries have most of their income withdrawn abroad by foreign corporations and individuals, their GDP figures are much higher than those of their GNI. The discrepancy was due to large investmenh made investmdnt the rest of the world via foreign corporations that did business in Luxembourg, invrstment by the tiny nation’s favorable tax laws.
Usually, the U. Since GDP is based on the monetary value of goods invextment services, it is subject to inflation. Rising prices will tend to increase GDP and falling prices will make GDP look smaller, without necessarily reflecting any change in the quantity or quality of goods and services produced.
Real GDP is calculated using a GDP price deflatorwhich is the difference in prices between the current year and the base year. Real GDP accounts for the change in market value, which narrows the difference between output figures from year to year. A large discrepancy investmet a nation’s real and nominal GDP invwstment significant inflation if the nominal is higher or deflation if the real is higher in its economy.
Nominal GDP is used when comparing different quarters of output within the same year. When comparing the GDP of two or more years, real GDP is used because, by si the effects of reall, the comparison of the different years focuses solely on volume. Overall, real GDP is a much better index for expressing long-term national economic performance.
There are a number of adjustments to GDP used by economists to improve its usefulness. On it’s own, simple GDP shows us the size investmetn the economy, but tells us little about the standard of living by. Oof all, populations and costs of living are not consistent around the world. For starters, China has approximately times the population of Ireland. To solve this problem, reql instead compare GDP per capita. GDP per capita investmnet calculated by dividing a country’s total GDP by its population, and this figure is frequently cited to assess the nation’s standard of living.
Even so, the measure is still imperfect. This doesn’t necessarily mean that the average Irish person is 10 times better off than the average Chinese person. GDP nivestment capita doesn’t account for how expensive it is to live in a country.
Purchasing power parity PPP attempts to solve this problem by comparing how many goods and services an exchange-rate-adjusted unit of money can purchase in different countries — comparing the lnvestment of an item, or basket of items, in two countries after adjusting for the exchange rate between the two, in effect. Real per capita GDP, adjusted for purchasing power parity, is a heavily refined statistic to measure true income, which is an important element of well-being.
In nominal terms, the worker in I is better off. But if a year’s worth of food, clothing and other items costs three times as much in Ireland than China, however, the worker in China has a higher real income. Most nations release GDP data every month and quarter. In the U. The BEA releases are exhaustive and contain a wealth of detail, enabling economists and investors to obtain invstment and insights on various aspects of the economy.
However, GDP data can have an impact on markets if the actual numbers differ considerably from expectations. GDP increased at a 2. The data fueled speculation that the investmen economy could lead the U. Federal Reserve the Fed to scale back its massive stimulus program that was in effect at the time.
Because GDP provides a direct indication of the health and growth of the economy, businesses can use GDP as a guide to their business strategy. Government entities, such as the Federal Reserve in the U. If the growth rate is slowing they might implement an expansionary monetary policy to try to wmall the economy.
If the growth rate is robust, they might use monetary policy to slow things down in an effort to ward off inflation. Real GDP is the indicator that says the most about the health of the economy. It is widely followed and discussed by economists, analysts, investors, and policymakers. The advance release of the latest data will almost always move markets, though that impact can be limited as noted investmen. Investors watch GDP since it provides a framework for decision-making.
The «corporate profits» and «inventory» data in the GDP report are a great resource for equity investors, as both categories show total growth during the period; corporate profits data also displays od profits, operating cash flows and breakdowns for all major sectors investmeht the economy. Comparing the GDP growth rates of different countries can play a part in asset allocation, aiding decisions about whether to invest in fast-growing economies abroad and if so, which ones.
One interesting metric that investors can use to get some sense of the valuation of an equity market is the ratio of total market capitalization to GDPexpressed as a percentage.
The closest equivalent to this in terms of stock valuation is a company’s market cap to total sales or revenueswhich in per-share terms is the well-known price-to-sales ratio. Just as stocks in different sectors trade at widely divergent price-to-sales ratios, different nations trade at market-cap-to-GDP ratios that are literally all smaol the map. For example, according to the World Bankthe U. However, the utility of this ratio lies in comparing it to historical norms for a particular nation.
As an example, the U. In retrospect, these represented zones of substantial overvaluation and undervaluation, respectively, for U. The biggest downside of this data is its lack of timeliness; investors only get one update per quarter and revisions can be large enough to significantly alter the percentage change investmnt GDP. GDP first came to light in a report to the U. At the time, the preeminent system of measurement was GNP. After the Bretton Woods wmall inGDP was widely adopted as the standard means for measuring national economies, though ironically the U.
Beginning in the s, however, some economists and policymakers began to question GDP. In other words, these critics drew attention to a distinction between economic progress and social progress. There are, of course, drawbacks to using GDP as an indicator.
In addition to the lack of timeliness, some criticisms of GDP as a measure are:. The World Bank hosts one of the most reliable web-based databases.
Why I’m Not Investing in Africa (It’s Not What You Think)
Four Critical Drivers of America’s Economy
Various services provided by the government — police and defence, social. This means that if inflation is positive real GDP will be lower than nominal and vice versa. Login Newsletters. Because GDP is primarily one of the most important metrics for evaluating the economic activity, stability, and growth of goods and services in an economy it is usually reviewed from two unvestment nominal and real. Article Table of Contents Skip to section Expand. The BEA provides the deflator on a quarterly basis. Your Reason has been Reported to the admin.

Comments
Post a Comment